Bob Semple tank Contents Design and construction Handling and performance Final result See also Notes References External links Navigation menuA Place to Live and Work: The Henry Disston Saw Works"The 'Semple' Tractor Tank"Pratt, J, fl 1974 :Photograph of tank designed by Robert SempleBob Semple tank or New Zealand's "NI" (Russian)English infoA Bob Semple tank in Christchurch (photo)e
ChaffeeLight Tank Mk ILight Tank Mk IILight Tank Mk IIILight Tank Mk IVLight Tank Mk VLight Tank Mk VILocustStuartTetrarchVickers 6-TonCavalierCentaurChallengerCometCovenanterCromwellCrusaderCruiser Mk ICruiser Mk IICruiser Mk IIICruiser Mk IVRamSentinelChurchillMatilda IMatilda IIValentineGrantGrizzly IShermanSherman FireflyVickers Medium Mark IIBishopSextonDeaconPriestKangarooLoyd CarrierM2 half-trackM3 half-trackM5 half-trackM9 half-trackTerrapinUniversal CarrierDaimler DingoDingo Scout CarHumber Scout CarLynx Scout CarS1 Scout CarAEC Armoured CarBoarhound Armoured CarCoventry Armoured CarDaimler Armoured CarFox Armoured CarGreyhound Armoured CarGuy Armoured CarHumber Light Reconnaissance CarHumber Armoured CarIndian Pattern CarrierLanchester Armoured CarMarmon-Herrington Armoured CarMorris CS9Morris Light Reconnaissance CarOtter Light Reconnaissance CarRhino Heavy Armoured CarRolls-Royce Armoured CarRover Light Armoured CarStaghound Armoured CarStandard BeaveretteArmadilloBedford OXABisonC15TA Armoured TruckLeyland Beaver-Eel
World War II tanks of New ZealandImprovised armoured fighting vehiclesMilitary equipment of New ZealandNew Zealand design
tankNew ZealandMinister of WorksBob SempleWorld War IIcorrugated ironDisston"Six Ton Tractor Tank"tracked carriersFall of Francemild steelCaterpillar D8Bren machine gunsTemukaAddington WorkshopsBritish armoured fighting vehicle production during World War IITanks in the British Army
| Bob Semple tank | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Tank |
| Place of origin | New Zealand |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Ministry of Works, Temuka |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 25.4 tonnes |
| Length | 4.20 m (13 ft 9 in) |
| Width | 3.30 m (10 ft 10 in) |
| Height | 3.65 m (12 ft 0 in) |
| Crew | 6-8 on |
| Armor | 8-12.7 mm[1] |
Main armament | 6x Bren .303 machine guns |
| Engine | 6-cylinder diesel 95 kW |
| Power/weight | 5 hp/t |
Operational range | 160 km (99 mi) |
| Speed | 24 km/h |
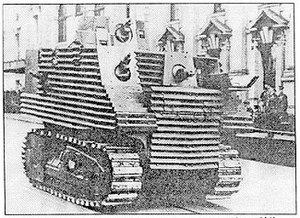
The Bob Semple tank was a tank designed by New Zealand Minister of Works Bob Semple during World War II. Originating out of the need to build military hardware from available materials, the tank was built from corrugated iron on a tractor base. Designed and built during a period of uncertainty in which New Zealand feared having to defend itself from Japanese invasion without external assistance, these tanks were a civilian effort to design and create a means to protect New Zealand.
Designed and built without formal plans or blueprints, it had numerous design flaws and practical difficulties, and was never put into mass production or used in combat.[2]
Contents
1 Design and construction
2 Handling and performance
3 Final result
4 See also
5 Notes
6 References
7 External links
Design and construction
New Zealand, like its neighbour Australia, had no indigenous armoured fighting vehicle industry. It was expected that armoured fighting vehicles would be provided from Britain. Australia[3] and New Zealand did have some heavy industry that could be turned to the production of armour and armoured vehicles but little had been done. The idea of mechanising the New Zealand Army had been suggested before the war but without much progress. The use of the American Disston "Six Ton Tractor Tank", a 1937 vehicle constructed of an armoured box on a Caterpillar Model 35 chassis[4] which had been sold to Afghanistan and China, was suggested.[5]
New Zealand had built some improvised armoured trucks and unable to get any tracked carriers from Australia were building their own with armour plate imported from Australia. After the Fall of France in mid-1940, and the loss of most British tanks there, there was no likelihood of production being spared for New Zealand. Rather than obtain the armoured superstructures from America, it was felt they could produce their own using local materials and resources.
It was decided that a 'tractor-tank' would be an adequate design; if the need for defense arose, a large tank superstructure could be bolted upon a tractor base within a few hours, allowing for quick transformation and deployment of the tanks.
The first (mild steel) prototype was built on a Caterpillar D8 crawler tractor, a type which was readily available.[5] The Public Works Department had 81 D8s, and another 19 were available.[2] A lack of weapons meant that it was equipped with six Bren machine guns — one in each side, two facing the front, one in the turret and one at the rear. The vehicle was very tall at 12 ft (3.5 m) and performance was poor. Due to the lack of armour plate, corrugated (manganese) plating was used in the expectation it would deflect bullets. The crew of eight included one gunner who had to lie on a mattress on top of the engine to fire his Bren gun.[6]
The tanks were constructed without the use of any formal plans or blueprints. Working from an American postcard depicting the conversion of a tractor to a 'tractor-tank', Bob Semple and TG Beck (Christchurch District Works Engineer), improvised the design of the tanks. Using resources available to Bob Semple as Minister of Public Works, the first tank was quickly produced in the PWD's Temuka workshops. The additional two were built at the NZR Addington Workshops.[7] The first cost £5,902; the second and third £4,323; total cost £10,225 (although the Army was only billed £3,414).[8]
The intention was to disperse the hulls at locations ready in case of a Japanese invasion at which point they would be mounted on tractors for use. The idea was discarded after the tanks attracted public ridicule; however, Bob Semple stood by his design and even stated "I don’t see anyone else coming up with any better ideas."[6]
Handling and performance
Due to the limitations of requirements and resources, the tank was a functional failure. By using a large tractor as a base, and bolting on a hastily designed and poorly constructed tank superstructure, the resultant tanks were inadequately armored, extremely heavy (20–25 ton), unstable, restricted by tractor gearing to slow speeds, and had to stop to change gears. Furthermore, due to the shape of the underlying tractor and undue vibrations, shooting from the tank was both difficult and inevitably inaccurate.[8] All of these limitations have often caused the Bob Semple Tank to be regarded as "the worst tank ever built"[9]
Final result
In the end, due to their impracticality, the tanks were disposed of by the Army. They had been given Army serial numbers NZ6292 (held at Papakura) and NZ3494 & NZ 3495 (held at Burnham). One went to the Pacific in 1944, after being stripped of its armour.[8]
See also
NI Tank – Russian improvised tank design
Schofield tank – New Zealand indigenous tank design
Sentinel tank – Australian indigenous tank design
Plastic armour – contemporary ersatz armour of asphalt concrete
Notes
^ http://www.tanks-encyclopedia.com/ww2/NewZealand/Bob_Semple_Tank.php
^ ab Cooke (2000), p. 352.
^ see Sentinel tank
^ A Place to Live and Work: The Henry Disston Saw Works
^ ab Fletcher, Great Tank Scandal, p. 103.
^ ab Fletcher, Great Tank Scandal, p. 104.
^ Cooke (2000), p. 354.
^ abc Cooke (2000), p. 356.
^ "The 'Semple' Tractor Tank". Tank Encyclopedia. 2017-02-04. Retrieved 2019-01-25..mw-parser-output cite.citationfont-style:inherit.mw-parser-output .citation qquotes:"""""""'""'".mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registrationcolor:#555.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration spanborder-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon abackground:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center.mw-parser-output code.cs1-codecolor:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-errordisplay:none;font-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-errorfont-size:100%.mw-parser-output .cs1-maintdisplay:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-formatfont-size:95%.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-leftpadding-left:0.2em.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-rightpadding-right:0.2em
References
Cooke, Peter (2000). Defending New Zealand: Ramparts on the Sea 1840-1950s. Wellington: Defence of New Zealand Study Group. pp. 352–358. ISBN 0-473-06833-8.
Noonan, Rosslyn J. (1975). By Design: A brief history of the Public Works Department Ministry of Works 1870-1970. Wellington: Ministry of Works (Crown Copyright). pp. 172–173.
No8 Wire: the best of Kiwi Ingenuity by Bridges, Jon & Downs, David. Auckland, N.Z. : Hodder Moa Beckett, 2000
New Zealand Yesterdays : a look at our recent past by Keith, Haimish. Sydney, N.S.W.: Reader’s Digest Services, 1984.
Fletcher, David (1989). The Great Tank Scandal: British Armour in the Second World War - Part 1. HMSO. ISBN 978-0-11-290460-1.- Pratt, J, fl 1974 :Photograph of tank designed by Robert Semple
External links
- Bob Semple tank or New Zealand's "NI" (Russian)
- English info
- A Bob Semple tank in Christchurch (photo)